Pediatric Dentistry
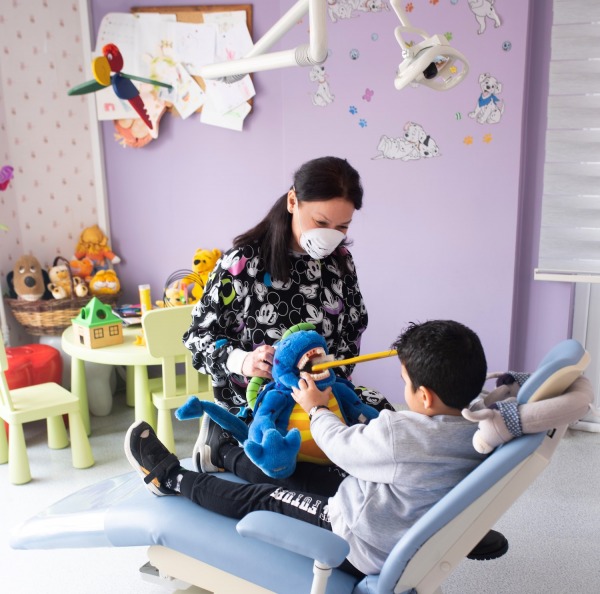
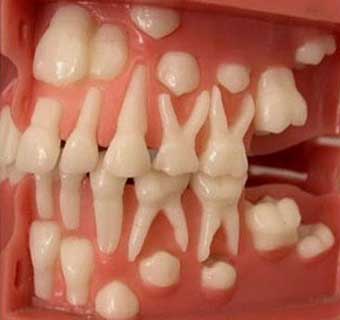
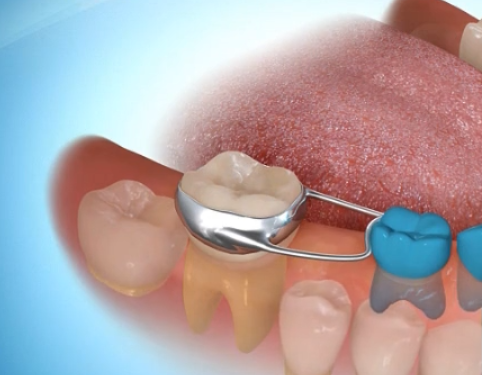
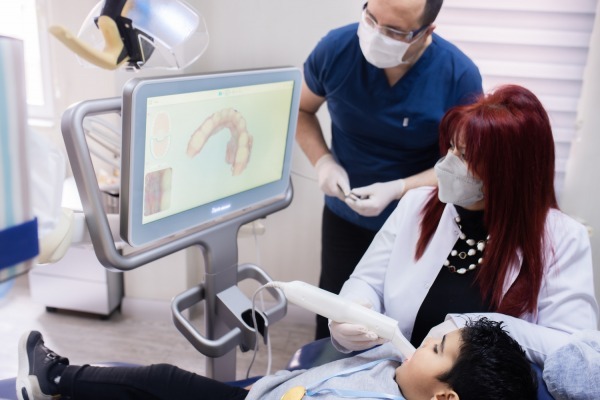
Pedodontics is the branch of dentistry that performs oral and dental health control, care and treatment from the birth of the baby until the end of mixed dentition; that is, until the average age of 12 years. It will be appropriate for your baby to be examined by a pediatric dentist 6 months after the first tooth erupts. During this examination, it is advisable to get information from your pediatric dentist on various issues such as your baby's nutrition, oral and dental care and sucking habits.
As children get older, routine examinations should be continued and no caries or pain should be expected. It is recommended that children meet the dentist at an early age and have regular check-ups, both for their oral and dental health and to prevent the development of "Dentist Fear".